Howto:Create WS3.0 terrain
| World Scenery 3.0 |
|---|
| General |
This article provides instructions on how to generate basic WS3.0 terrain.
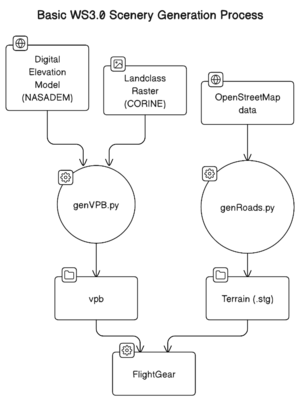
WS3.0 terrain consists of three parts:
- A terrain mesh consisting of a landclass texture draped over an elevation model.
- A high resolution water raster used to show water features such as rivers, lakes and coastline with more definition
- Line features such as roads and railways.
The terrain is generated by a set of tools that are packaged in a docker image for convenience.
Prerequisites
Set up a Workspace
Create a directory with the following sub-directories:
cachedataoutput/vpboutput/Terrain
Docker
- Install Docker on your platform.
- Pull the docker image by running the following command
docker pull flightgear/ws30-vpb-generator:latest
Optionally, if you are hitting rate limits:
- Create an account on https://hub.docker.com/. (Note that you will need to click on an email verification link before you can log in for the first time)
- Run
docker loginbefore the docker pull command above
Getting the base data
You need two pieces of data for the area of scenery you are generating:
- An elevation model (aka DEM). This indicates what altitude each point of the surface is.
- Landclass data showing what type of terrain is at each point of the surface. This is often either a Raster (effectively a texture), or vector data.
Elevation Model
Download the NASADEM elevation model for the area of scenery you wish to generate. This is available in 1x1 degree blocks from here, and with an interactive browser here.
Unzip the files into the data directory.
Landclass Raster
Download an landclass raster for the area of scenery you wish to generate.
- For Europe, use of CORINE is recommended.
- For the USA NLCD is recommended
- Sentinel-2 data is available for the entire world via ESRI, but has limited set of landclasses.
Put these into the data directory.
More detailed terrain can be created by modifying the landclass raster, and/or generating a new raster from vector data. These processes are discussed below.
Generating Terrain
To generate terrain you need to run the tools within the docker container we installed above. The docker image is like a small, independent virtual computing environment running within your system. This particular docker image has all the scenery generation tools already installed.
Running the docker container
Firstly, get the container running from the directory containing your cache, data and output directories:
docker run --rm --mount "type=bind,source=`pwd`/data,target=/home/flightgear/data,readonly" --mount "type=bind,source=`pwd`/output,target=/home/flightgear/output" --mount "type=bind,source=`pwd`/cache,target=/home/flightgear/cache" -it flightgear/ws30-vpb-generator:latest /bin/bash
You should now find yourself in a bash shell within your container. You should see data and output directories which are linked to the directories you created earlier:
flightgear@ddcac77f7d5e:~$ ls cache data output bin scripts
Building the terrain
To build the terrain mesh, use the genVPB.py tool from inside the docker container.
Usage: genVPB.py --raster <input-raster> [ option ... ]
Usage: genVPB.py --bbox <lat0> <lon0> <lat1> <lon1> --sentinel --reclass <reclass> [ option ... ]
Arguments:
--raster <input-raster> - Input landclass raster
--bbox <lat0> <lon0> <lat1> <lon1> - Bounding box of scenery to be generated.
--sentinel <raster-dir> - Using Sentinel-2 Landclass data from <raster-dir>
--auto-download - Auto-download Sentinel-2 Landclass data. Only valid with --sentinel
--hgt-dir <hgt-dir> - Set directory containing unzipped NASADEM HGT files. Defaults to '{DEFAULT_HGT_DIR}'.
--output-dir <output-dir> - Set output directory. Defaults to '{DEFAULT_OUTPUT_DIR}'.
--reclass <reclass> - Reclassify raster using file <reclass>. See fgmeta/ws30/mappings/.
--coastline <coastline> - Clip against coastline against polygon (.osm). E.g. from https://osmdata.openstreetmap.de/data/land-polygons.html.
--shrink-water <pixels> - Shrink water bodies (landclasses 40, 41) by <pixels> pixels, typically in combination with generating a water raster.
--generate-water-raster - Generate a water raster from OSM data.
--cache-dir <dir> - Use <dir> as a cache of OSM data to improve performance and reduce load on Overpass API.
--nasadem-server <server> - Set server to download NASADEM data from. Defaults to {getNASADEM.DEFAULT_SERVER}
--nasadem-user <user> - NASA Earthdata username. Required to download NASADEM automatically. To create a username, see https://urs.earthdata.nasa.gov/users/new/.
--nasadem-password <password> - NASA Earthdata password. Required to download NASADEM automatically.
--debug - Debug output, generate intermediate geoTIFFs and don't compress output.
For example, to generate a piece of terrain around Edinburgh (latitude 55.5, longitude 3 degrees West)
./scripts/genVPB.py --bbox -55 -3 56 -2 --raster ./data/uk_wgs84_10m_N54.tif
If you are using anything other than a CORINE raster you will need to reclassify the data to match the landclasses used by FlightGear. Those classes are defined in Materials/base/landclass-mapping.xml. You can reclassify them using the files in the scripts/mappings directory. E.g. to reclassify NLCD2019 data you can use --reclassify ./scripts/mappings/nlcd2019.txt.
genVPB.py will output the data to the output/vpb directory, in which you should find a series of files and directories.
Adding water
The terrain mesh does not have highly detailed water features - as typically the source data has a resolution of 10-25m. Water features are generated from OpenStreetMap data. To generate water features simply run the genwaterraster.py command.
Usage: genwaterraster.py <min-lat> <min-lon> <max-lat> <max-lon> <scenery-dir> [cache-dir]
<min-lat> <min-lon> <max-lat> <max-lon - bounding box of water to generated <scenery_dir> Scenery directory to write to [Cache] Optional directory to cache OpenStreetMap data to reduce API requests
The scenery directory should be your output/vpb directory created above. For example, to generate water for the area around Edinburgh:
./scripts/genwaterraster.py 55 -4 56 -3 ./output/vpb ./cache
Inside the ./output/vpb directory there should be a set of directories and .png files.
Adding roads and railways
The terrain mesh does not have any line features - things like roads. These are generated separately from OpenStreetMap data. To generate line features simply run the genroads.py command:
Usage: ./scripts/genroads.py <scenery_dir> <lon1> <lat1> <lon2> <lat2> [Cache] <scenery_dir> Scenery directory to write to <lon1> <lat1> Bottom left lon/lat of bounding box <lon2> <lat2> Top right lon/lat of bounding box [Cache] Optional directory to cache OpenStreetMap data to reduce API requests
The scenery directory should be your output/Terrain directory created above. For example, to generate roads for the area around Edinburgh:
./scripts/genroads.py ./output/Terrain -4 55 -3 56 ./cache
Inside the ./output/Terrain directory there should be a set of directories and, .STG files text files.
Running FlightGear with the new WS3.0 Terrain
To test the new terrain, simply include the output directory in your scenery path and run FlightGear with the --prop:/scenery/use-vpb=true to enable WS3.0.
Advanced Techniques
The following sections describe more complex techniques to generate higher quality WS3.0 terrain. Almost all of them involve using different data sources to generate a more detailed landclass raster before running the final scenery generation processes described above. Generating a highly detailed landclass raster is where the magic happens.
Most techniques use gdal or grass to modify the raster/vector data, typically using the QGIS program.
Using a different elevation model
If you are using another elevation model other than NASAEM, then you may need to re-project it using QGIS/gdalwarp to the WGS84 CRS (aka EPSG:4326).
Landclass Data Requirements
For any landclass data we need to ensure the data is in the correct format. That means:
- Is a Raster (geotiff) rather than Vector data. This raster will become the texture on the terrain that the terrain shaders do their magic on.
- Uses the WGS84 Coordinate Reference System. The ensures that the terrain generation step is efficient.
- Has the correct landclass values for each terrain type. We use a set of values based on the CORINE raster set, defined in Materials/base/landclass-mapping.xml.
Below is a quick table showing what steps you need to take for common landclass data sources.
| Landclass Data | Warp to WGS84 required? | Landclass re-classification Required? | Raster Simplification Required? | Conversion to Raster Required? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CORINE Raster | Yes | No | No | No |
| CORINE Vector | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| NLCD | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Sentinel-2 | Yes | Yes | No | No |
Conversion to Raster must be done manually. Converting to WGS84 and the correct landclasses can be done by the genVPB.py script, but slows down scenery generation. Therefore if you are planning to generate scenery multiple times it is best to pre-process the files yourself.
The easiest way to do these operations is using QGIS, which is available for most platforms. If you are scripting a toolchain, the QGIS tools include command-line equivalents for all commands.
When using QGIS, set the Project CRS to WGS84 (aka EPSG:4326). You can then add layers of Raster or Vector data from files from the Layer->Add Layer menu. When performing any operations, always write out the data to a real file so you can go back to it later. Disk space is cheap :).
Warping Raster Layers to WGS84
genVPB.py will automatically convert to WGS84 if it detects a landclass raster with a different Coordinate System. However, you may wish to do so manually instead so all your data is on the same coordinate system.
In QGIS you can warp a raster layer to a different CRS using the Raster->Projections-Warp (Reproject) tool.
Select the following options in the dialog:
- Input Layer - Check you have selected the correct layer. The CRS is shown at the right.
- Target CRS - set to
EPSG:4326 - WGS84, which should be your project CRS. - Resampling Method to Use - Nearest Neighbour. (Landclass data is not like normal images. You don't want to interpolate between values.)
- Nodata value for output bands - 0.0 (This means that any data at the edges will be Ocean, usually a reasonable default)
- Advanced Parameters - No Compression
- Output data type - Byte
- Reprojected - Choose a target filename
Alternatively you can do this step from the commandline.
gdalwarp -t_srs EPSG:4326 -dstnodata 0.0 -r near -ot Byte -of GTiff -co COMPRESS=NONE -co BIGTIFF=IF_NEEDED /home/stuart/FlightGear/VPB/data/CORINE/u2018_clc2018_v2020_20u1_raster100m/DATA/U2018_CLC2018_V2020_20u1.tif /home/stuart/FlightGear/VPB/data/scratch/corine_WGS84.tif
Warping Vector Layers to WGS84
genVPB.py will automatically convert to WGS84 if it detects a landclass raster with a different Coordinate System. However, you may wish to do so manually instead so all your data is on the same coordinate system.
In QGIS you can warp a vector layer using Vector->Data Management Tools->Reproject Layer.
Set the following options in the dialog:
- Input Layer - Check you have selected the correct layer. The CRS is shown at the right.
- Target CRS - set to
EPSG:4326 - WGS84, which should be your project CRS. - Reprojected - Choose a target filename
Reclassifying Vector Layers
For CORINE vector data in particular, the attributes used in the vector data are not the same as those used by the CORINE Raster data. So we need to create a new attribute on the data.
To do this
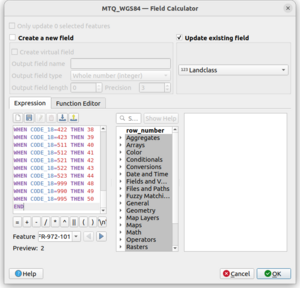
- Select
Layer->Open Attribute Table. You should see a table with multiple columns. Each row represents a feature in the data. - Click on
Toggle Editing Mode(Ctrl + E), on the top left of the dialog - Click on
New Field(Ctrl+W) and create a new field called Landclass of type "Whole Number (Integer)". This will create a new column which we will populate with the correct landclass data - Click on the
Open Field Calculatorbutton (Ctrl + I). (If you get an error about only being able to create Virtual fields, go back to the Layer menu, export it and open the exported file). - Select the following options:
- Update Existing Field
- Select the Landclass field you just created.
- Copy the contents of https://sourceforge.net/p/flightgear/fgmeta/ci/next/tree/ws30/mappings/corine_vector.txt into the Expression box (without the comment lines starting with
#). This is just some simple code to set the attribute correctly. The code should be correct for CORINE vector data. If your data is from other sources you will need to work out how you want to map your source data landclasses to the CORINE ones. Materials/base/landclass-mapping.xml can be used as a guide.
- Select
OK. You should see that your landclass column is now populated with the landclass data. - Select
Layer->Save Layer Editsto save you changes
Creating a Raster from a Vector Layer
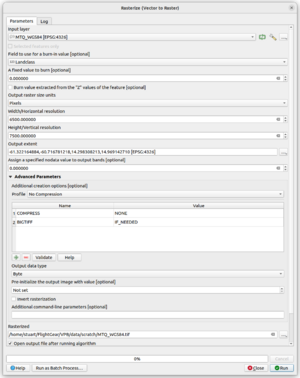
To create a Raster from a Vector Layer select Raster->Conversion->Rasterize (Vector to Raster).
Select the following options:
- Input Layer - correct layer, check CRS
- Field to use for burn-in value - select the
Landclasscolumn you created above. - Output raster size units. This is going to set the resolution of your raster. You can work out the resolution in two different ways:
- Select "Georeferenced units" and determine how many degrees each pixel is in latitude and longitude.
- Select "Pixels" and determine the size of raster you want in pixels. This is a good calculator to help. You input e.g. SE and SW coordinates and calculate to get the distance in Km. Then you multiply by thousand and devide by the number of metres per pixel (e.g. 5) -> resolution for width.
- Width/Horizontal Resolution. Enter the values you've calculated for the horizontal resolution (longitudinal), or the width of the raster
- Height/Vertical Resolution. Enter the values you've calculated for the vertical resolution (latitude or the height of the raster)
- Output extent - Select an option from the box on the right. You can edit the text afterwards (NB: East, West, South, North). Best practise is to create long thin strips of 1 degree latitude in height, as this makes subsequent processing much easier.
- Assign a specific nodata value to output bands - Select 0.0 for Ocean. CORINE vector data in particular has a lot of nodata for Oceans
- Advanced Parameters - No Compression
- Output data type - Byte
- Rasterized - Select a new filename
Simplifying a Raster Layer
Some Raster Landclass data (NLCD included) has too much noise - in particular large US highway systems are identified as Urban areas.
To smooth it out we can use the GRASS n.neighbors function from the Processing Toolbox in QGIS.
Select the following options:
- Input Layer - correct layer, check CRS
- Neighborhood operation - median. (This is not a normal image, so using an average will result in weird values)
- Neighborhood size - 5.
- Neighbors - Select a new filename.
Clipping a Raster Layer with OSM Data for Land (Corine)
The Corine dataset does not match OSM coastlines exactly. The following multi-stage process makes sure, that no Corine land-use is in the water as defined by OSM.
Download OSM Land Data
Download land polygons based on OSM data as a Shapefile from Land Polygons and make sure to pick the WGS84 projected download with split polygons ("Large polygons are split, use for larger scales"). Once downloaded unzip the content into a directory.
Reclassifying the OSM Land Data Vector Layer
I QGIS make sure that only the layer for the raster for land data is selected (e.g. land-polygons-split-4326) -> in the map view you will see the whole earth. NB: typically you do this reclassify only once after download and can reuse the result for future processing.
Then:
- Select
Layer->Open Attribute Table. You should see a table with multiple columns. Each row represents a feature in the data. - Click on
Toggle Editing Mode(Ctrl + E), on the top left of the dialogue - Click on
New Field(Ctrl+W) and create a new field called Landclass of typeInteger (32 bit). This will create a new column which we will populate with the correct land class data - On top of the table on the left side choose "Landclass" in the drop-down menu, then input
2into the field to the right and then press button "Update" all to the left of this field. - Wait a bit and the close the dialogue.
- Select
Layer->Save Layer Editsto save your changes (overwrite e.g.land-polygons-split-4326).
Convert the Land Data from Vector to Raster
Do the same as in chapter "Creating a Raster from a Vector Layer" above. The only difference is that the Input layer will be the land data polygons and you need to choose a different file name for the "Rasterized" (e.g. osm_land_scotland_5m.tif)
Remove Novalue Entries in the Land Data Raster
To do this:
- Select
Processing->Toolbox. You should see a new box on the right side. - Write "gdal_calc" in the search box and you should see an entry "Raster calculator". Double click on it and you will get a new dialogue window.
- In this dialogue:
- For "Input layer A" choose the raster from the previous chapter ((e.g. osm_land_scotland_5m.tif)
- In field "Calculation in gdalnumeric ..." write:
greater(A,0) * A - In field "Output raster type" choose
Byte - In field "Advanced Parameters" choose Profile
No compression - In field "Additional command-line parameters" write:
--hideNoData - In field "Calculated" choose a file (e.g. osm_land_scotland_allvalues_5m.tif)
- (In the "GDAL/OGR console call" it will have something similar to the follwing - just with different paths:
gdal_calc.py --overwrite --calc "greater(A ,0) * A" --format GTiff --type Byte -A /home/vanosten/custom-fg-scenery/data/osm_land_scotland_5m.tif --A_band 1 --co COMPRESS=NONE --co BIGTIFF=IF_NEEDED --hideNoData --outfile /home/vanosten/custom-fg-scenery/data/osm_land_scotland_allvalues_5m.tif - Press the "Run" button - and when complete close the dialogue.
You should now see a map only black and white. You can check for correctness by pressing CTRL+SHIFT+I to get a cursor with an arrow and an "i". First make sure the new raster is selected on the left side. Next click on the sea/ocean and then check in the "Identify Results" window on the right that the value is < 2. The click on the land and check that the value is 2.
Create the Final Clipped Corine Raster Against OSM Land Data =
Do the following:
- In QGIS make sure that you have only the following two layers: the basis Corine raster (see chapter "Creating a Raster from a Vector Layer" - here e.g. corine_raster_scotland_5m.tif) and plus the raster from the previous step (e.g. osm_land_scotland_allvalues_5m.tif)
- Select
Raster->Raster Calculator ...and a corresponding dialogue will open showing on the left hand side the two rasters. - Choose a new "Output layer" (e.g. corine_raster_scotland_clipped_5m.tif).
- In the "Raster Calculator Expression" field input:
if ("osm_land_scotland_all_data_5m@1" < 2, 44, "corine_raster_scotland_5m@1") - Press button "OK" and wait a while (you will see a new dialogue with showing the progress.
Done. You have now a raster (e.g. corine_raster_scotland_clipped_5m.tif) which does not have land in areas, where OSM data has sea/ocean.
Reclassifying a Raster Layer
WS3.0 uses CORINE landclass values. If using data from other sources it needs to be reclassified to the correct values. genVPB.py has an option to do this, but you may wish to do so manually.
To do this select GRASS->Raster->r.reclass from the Processing Toolbox.
Select the following options:
- Input Raster Layer - correct layer, check CRS
- Reclass rules text - copy in the contents of https://sourceforge.net/p/flightgear/fgmeta/ci/next/tree/ws30/mappings/nlcd2019.txt. Or an appropriate mapping from your landclass data to CORINE. Note that you can also reference a file using the "File containing reclass rules" option. Note a mapping of 22 24 = 1 is the same as 22 and 24 = 1. For a range of 22 to 24 use 22 23 24 = 1.
- Reclassified - Select a new filename.
(If this doesn't work a similar function is available in the Processing Toolbox under Raster analysis->Reclassify by table. However this doesn't save your table once you close the dialog, and entries have to be manually entered individually which takes a lot of effort)
Step By Step Procedure for Processing NLCD for the USA using the Raster Calculator, Up sampling and GRASS r.neighbors
NOTE: This "raster calculator" process or method is considered suboptimal to the Python script method below. The Python script method below has newer smoothing processes. However, this method does contain useful knowledge on how to use the raster calculator. It needs to be updated to match the Python script method.
We will use a predetermined file naming convention throughout this procedure for simplicity. You can use a naming convention of your choice.
The below python script produces more refined scenery than this method. I left this documentation though as it is a good starting point and has examples of how you can manipulate rasters using the calculator. It was the first steps I took to learn how all this stuff works. It could be updated to match all the steps used in the python script method.
Obtain your NLCD_2019_Land_Cover from source of choice, https://www.mrlc.gov/viewer/
NLCD_2019_Land_Cover data = NLCD_2019_Land_Cover_California-Southern.tiff
Obtain your NLCD_2016_Tree_Canopy from source of choice, https://www.mrlc.gov/viewer/
NLCD_2016_Tree_Canopy data = NLCD_2016_Tree_Canopy_California-Southern.tiff
Make Deciduous Layer 255 to 0 EPSG:5070 - NAD83 - Raster Calculator
("NLCD_2016_Tree_Canopy_California-Southern@1" = 255) * 0 + ("NLCD_2016_Tree_Canopy_California-Southern@1" != 255) * "NLCD_2016_Tree_Canopy_California-Southern@1"
Output CRS = EPSG:5070 - NAD83
Output Layer = California-Southern_deciduous-coast-clipped.tiff
OK
Make Tree Canopy Layer EPSG:5070 - NAD83 - Raster Calculator
Use the prevailing tree type, for Deciduous use * 41, for Evergreen use * 42, for MixedForest use 43.
Later we add this Tree Canopy layer to the raster where there is currently no trees in the NLCD
If ocean bordering with index 255 -
("California-Southern_deciduous-coast-clipped@1" != 0) * 42
Else
("NLCD_2016_Tree_Canopy_California-Southern@1" != 0) * 42
Output CRS = EPSG:5070 - NAD83
Output Layer = California-Southern_deciduous.tiff
OK
Make Clipped Ocean Frontage EPSG:5070 - NAD83 - GIMP
Source = NLCD_2019_Land_Cover_California-Southern.tiff
Flood fill index 11 (blue) with 0 (black)
Export tiff = California-Southern_coast-clipped.tiff
Warp NLCD Deciduous and Base NLCD from EPSG:5070 - NAD83 / Conus Albers NLCD to Project CRS: EPSG:4326 - WGS 84 - WARP
If ocean bordering with index 255
Warp California-Southern_coast-clipped.tiff
Else
Warp NLCD_2016_Tree_Canopy_California-Southern.tiff
and
Warp Deciduous NLCD from EPSG:5070 - NAD83 / Conus Albers NLCD to Project CRS: EPSG:4326 - WGS 84
Warp California-Southern_deciduous.tiff
Raster -> Projection - > Warp
Target CRS = EPSG:4326 - WGS 84
Resampling method to use = Nearest Neighbour
Output data type = byte
Reprojected = California-Southern_4326-84.tiff and California-Southern_deciduous_4326-84.tiff
Run
Combine "California-Southern_deciduous_4326-84.@1" and "California-Southern_4326-84@1" - Raster Calculator
This step adds the Tree Canopy layer to the existing NLCD raster only where there is currently no existing tree land cover.
(("California-Southern_4326-84@1" > 0 AND "California-Southern_4326-84@1" != 41 AND "California-Southern_4326-84@1" != 42 AND "California-Southern_4326-84@1" != 43) AND "California-Southern_deciduous_4326-84@1" > 0) * "California-Southern_deciduous_4326-84@1" + ("California-Southern_4326-84@1" = 41 OR "California-Southern_4326-84@1" = 42 OR "California-Southern_4326-84@1" = 43 OR "California-Southern_deciduous_4326-84@1" <= 0) * "California-Southern_4326-84@1"
Output CRS = EPSG:4326 - WGS 84
Output Layer = California-Southern_adjusted.tiff
OK
Re-class urban 21, 22, 23, 24 = grass 26 - Raster Calculator
This step is being used to erase all the man made clutter on the raster with grassland. Instead of grassland you can replace it with any type of prevailing groundcover in the area your processing.
For example this places a road easement of grass on all the road clutter that was originally in the raster. If your processing a desert area you might want to use dirt or sand instead of grassland. For Arctic areas maybe use tundra.
Part of the clutter gets replaced later in the process.
("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 11) * 41 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 12) * 34 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 21) * 26 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 22) * 26 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 23) * 26 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 24) * 26 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 31) * 27 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 41) * 26 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 42) * 24 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 43) * 25 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 51) * 30 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 52) * 29 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 71) * 26 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 72) * 32 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 73) * 31 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 74) * 31 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 75) * 32 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 81) * 18 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 82) * 19 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 90) * 25 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 95) * 35
Output CRS = EPSG:4326 - WGS 84
Output Layer = California-Southern_reclass-grass.tiff
OK
Make Urban layer
("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 21) * 10 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 22) * 1 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 23) * 1 + ("California-Southern_adjusted@1" = 24) * 2
Output CRS = EPSG:4326 - WGS 84
Output Layer = California-Southern_urban.tiff
OK
Remove the road clutter with r.neighbor
GRASS/Raster/r.neighbor
Neighborhood operation = median
Neighborhood size = 7
Neighbors = California-Southern_urban-only.tiff
Run
Combine "California-Southern_reclass-urban@1" and "California-Southern_reclass-grass@1"
This step replaces the "cleaned up" urban areas back into the raster.
("California-Southern_urban-only@1" < 1) * "California-Southern_reclass-grass@1" + ("California-Southern_urban-only@1" != 0) * "California-Southern_urban-only@1"
Output CRS = EPSG:4326 - WGS 84
Output Layer = California-Southern_adjusted-combined.tiff
OK
Up sample California-Southern_adjusted-combined.tiff 2x, 4x or 8x resolution 0.00008309125
Active Layer = California-Southern_adjusted-combined.tiff
Layer/Save As
2x Horizontal = 0.00008309125
2x Vertical = 0.00008309125
4x Horizontal = 0.00010637625
4x Vertical = 0.00010637625
8x Horizontal = 0.00005318812
8x Vertical = 0.00005318812
File Name = California-Southern_final-prep-4x.tiff
OK
Simplify California-Southern_4326-84-hd.tiff with r.neighbor
GRASS/Raster/r.neighbor
Neighborhood operation = median
Neighborhood size = 7
Neighbors = California-Southern_urban-only.tiff
Run
Reclass index 0 to 44, leave the rest the same
("California-Southern_4326-84-hd@1" = 0) * 44 + ("California-Southern_4326-84-hd@1" != 0) * "California-Southern_4326-84-hd@1"
Output CRS = EPSG:4326 - WGS 84
Output Layer = California-Southern_4326-84-hd-corrected.tiff
OK
Optional HD Fresh Water Option
- Step 1 - Obtain and load hi resolution vector layer
Make sure that the vector layer and the raster layer you will eventually merge to have the same projection. ** Extent can be different if you use the option below.
- Use Top Menu: "Raster" -> "Conversion" -> "Rasterize (vector to raster)" or Processing Toolbox: GDAL -> "Vector conversion" -> "Rasterize (vector to raster)"
- Input layer = Southern-California_water_4326-84
- Fixed value to burn = 41 (water)
- Output raster size units = "Georeferenced units"
- Width/Horizontal resolution = 0.00008309125 (4x the base NLCD resolution )
- Height/Vertical resolution = 0.00008309125 (4x the base NLCD resolution)
- ** Output extent = Select the raster layer you will eventually merge with as the "Output extent".
- Under "Rasterized" choose a new filename to save the new raster to. We'll use Southern-California_4326-84-hd-water.tiff.
Click "Run" to generate the hi resolution raster layer.
- Step 2 - Reclass hi res, smoothed water to grass
- Open Raster Calculator
- Under "Output layer" choose a new filename to save the new raster to. We'll use Southern-California_4326-84-hd-nowater.tiff.
- Copy the following into the "Raster Calculator Expression" box. Where Southern-California_4326-84-hd is the name of your hi resolution, smoothed NLCD that includes the water data.
"Southern-California_4326-84-hd@1" * ("Southern-California_4326-84-hd@1" != 41) + 26 * ("Southern-California_4326-84-hd@1 = 41")
Click on "OK". When finished you will have a new raster with the water layer changed to grassland. Another choice would be to change it to sand.
- Step 3 - Combine the hi resolution no water raster and the hi resolution water raster.
- Use Top Menu: "Raster" -> "Miscellaneous" -> "Merge" or Processing Toolbax: GDAL -> Raster Miscellaneous -> Merge
- Input layers = Select "Southern-California_4326-84-hd-nowater@1" and Southern-California_4326-84-hd-water.tiff
- Output data type = "byte".
- Under "Merged" choose a new filename to save the new raster to. We'll use Southern-California_4326-84-hdwater.tiff.
Click "Run" to generate the new merged hi resolution raster layer.
Optional Python script to process NLCD for the USA
You can optionally process the NLCD by loading this script in the python console of the QGIS Desktop program. This python script method produces more refined data than by using the python calculator method above and it is more automated. If you run this script outside the python console you will need to modify it to locate the data you are processing. If you save the NLCD tiff's using the same consistent naming convention used in this example it is fairly simple to generate final WS3.0 tiff's to use to generate the scenery.
You will start with an original tree layer and a land cover layer from the MRLC.gov site. See the section "Obtaining NLCD" in the above "Step By Step Procedure for Processing NLCD for the USA using the Raster Calculator" topic.
For example, to start with you will have a couple files named...
NLCD_2016_Tree_Canopy_Alaska141-140_60.tiff
NLCD_2016_Land_Cover_Alaska141-140_60.tiff
In the QGIS program the layer names you start with will be...
NLCD_2016_Tree_Canopy_Alaska141-140_60
NLCD_2016_Land_Cover_Alaska141-140_60
which will refer to the tiff files.
Running this script will generate a bunch of intermediate files including the last file, that will be the final finished file for running in the VPB script or VPB build environment Docker image.
The last file for this example for New York would be, NLCD_2016_Alaska141-140_60_Smoothed-HD-Compressed_4326.tiff
from qgis.core import QgsApplication, QgsCoordinateTransform, QgsProject, QgsRasterLayer, QgsCoordinateReferenceSystem, QgsProcessingException, QgsRasterBlock, QgsRectangle
from qgis.analysis import QgsRasterCalculator, QgsRasterCalculatorEntry
from qgis import processing
from processing.core.Processing import Processing
from osgeo import gdal, osr, ogr
import os
import numpy
import numpy as np
import subprocess
# Define input layer names, change according to your file names
path = 'G:/Scenery/ws3.0/';
year = '2016';
state = 'Alaska';
part = '141-140_60';
################################## IMPORTANT ###############################
# Beginning filename of the NLCD from the source needs to be
# NLCD_' + year + '_Tree_Canopy_' + state + part + '.tiff'
# Also note that "/data/" is hardcoded into the path as well
# I needed the existing path structure to process it by state.
# For Alaska I used one lat and a few lon sections per chunck built.
# I will likly do the entire NLCD coverage area the same in future runs.
# Example beginning NLCD source:
# NLCD_2016_Tree_Canopy_Alaska141-140_60.tiff
# Full path and filename to source example is:
# G:/Scenery/ws3.0/Alaska/data/NLCD_2016_Tree_Canopy_Alaska141-140_60.tiff
# Final output path to last processed file is:
# G:/Scenery/ws3.0/Alaska/data/NLCD_2016_Alaska141-140_60_Smoothed-HD-Compressed_4326
#IMPORTANT NOTE:
# On any subprocess.run(command, shell=True) process, when using the script in Linux
# you need to change to subprocess.run(command). Remove the shell=True.
#You can try using the following syntax for both Windows and Linux
#subprocess.run([
# 'gdal_calc.py',
# '-A', input_path,
# '--outfile', output_path,
# '--calc', expression,
# '--type', 'Byte'
#], check=True)
############################################################################
################################################## Step 1: Reclass tree canopy to one landcover type 41, 42, or 43 #########################################
#FG NLCD
#23 DeciduousBroadCover 41
#24 EvergreenForest 42
#25 MixedForest 43
# Define input and output paths
input_path = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_Tree_Canopy_' + state + part + '.tiff'
output_path = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Trees-Combined.tiff'
expression = (
'((A > 0) & (A < 255)) * 43 + '
'(A <= 0) * A'
)
command = [
'gdal_calc.py',
'-A', input_path,
'--outfile', output_path,
'--calc', expression,
'--type', 'Byte'
]
subprocess.run(command, shell=True)
print("Step 1: Calculate result_tree_canopy completed. (NLCD_" + year + "_" + state + part + "_Trees-Combined)")
############################################################# Step 2: Warp tree canopy to 4326 #############################################################
input_path = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Trees-Combined.tiff'
output_path = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Tree_Canopy_4326.tiff'
processing.run(
"gdal:warpreproject",
{
'INPUT':input_path,
'SOURCE_CRS':None,
'TARGET_CRS':QgsCoordinateReferenceSystem('EPSG:4326'),
'RESAMPLING':0,
'NODATA':None,
'TARGET_RESOLUTION':None,
'OPTIONS':'',
'DATA_TYPE':1, # GDAL GDT_Byte
'TARGET_EXTENT':None,
'TARGET_EXTENT_CRS':None,
'MULTITHREADING':False,
'EXTRA':'',
'OUTPUT':output_path
}
)
print("Step 2: Warp tree_canopy completed. (NLCD_" + year + "_" + state + part + "_Tree_Canopy_4326)")
################################################################### Step 3: Warp land cover 4326 ############################################################
input_path = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_Land_Cover_' + state + part + '.tiff'
output_path = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Land_Cover_4326.tiff'
processing.run(
"gdal:warpreproject",
{
'INPUT':input_path,
'SOURCE_CRS':None,
'TARGET_CRS':QgsCoordinateReferenceSystem('EPSG:4326'),
'RESAMPLING':0,
'NODATA':None,
'TARGET_RESOLUTION':None,
'OPTIONS':'',
'DATA_TYPE':1, # GDAL GDT_Byte
'TARGET_EXTENT':None,
'TARGET_EXTENT_CRS':None,
'MULTITHREADING':False,
'EXTRA':'',
'OUTPUT':output_path
}
)
print("Step 3: Warp land_cover completed. (NLCD_" + year + "_" + state + part + "_Land_Cover_4326)")
################################################################ Step 4: Combine land cover 4326 and tree canopy 4326######################################
input_path_a = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Tree_Canopy_4326.tiff'
input_path_b = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Land_Cover_4326.tiff'
output_path = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Tree_Land_Combined_4326.tiff'
expression = (
'(((B > 0) & (B < 255)) & (B != 41) & (B != 42) & (B != 43) & (A > 0)) * A + '
'((B == 41) | (B == 42) | (B == 43) | (A <= 0)) * B'
)
command = [
'gdal_calc.py',
'-A', input_path_a,
'-B', input_path_b,
'--outfile', output_path,
'--calc', expression,
'--type', 'Byte'
]
subprocess.run(command, shell=True)
print("Step 4: Combine tree canopy and land cover completed. (NLCD_" + year + "_" + state + part + "_Tree_Land_Combined_4326)")
############################################################## Step 5: Replace urban and clutter with grass ###################################################
input_path = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Tree_Land_Combined_4326.tiff'
output_path = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Grass-Only_4326.tiff'
expression = (
'(A == 0) * 44 + '
'(A == 11) * 44 + '
'(A == 12) * 34 + '
'(A == 21) * 26 + '
'(A == 22) * 26 + '
'(A == 23) * 26 + '
'(A == 24) * 26 + '
'(A == 31) * 27 + '
'(A == 41) * 23 + '
'(A == 42) * 24 + '
'(A == 43) * 25 + '
'(A == 51) * 30 + '
'(A == 52) * 29 + '
'(A == 71) * 26 + '
'(A == 72) * 32 + '
'(A == 73) * 31 + '
'(A == 74) * 31 + '
'(A == 75) * 32 + '
'(A == 81) * 18 + '
'(A == 82) * 19 + '
'(A == 90) * 25 + '
'(A == 95) * 35'
)
command = [
'gdal_calc.py',
'-A', input_path,
'--outfile', output_path,
'--calc', expression,
'--type', 'Byte'
]
subprocess.run(command, shell=True)
print("Step 5: Replace urban and clutter with grass completed. (NLCD_" + year + "_" + state + part + "_Grass-Only_4326)")
################################################################## Step 6: Reclass urban 21, 22, 23 or 24 ###########################################################
input_path = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Tree_Land_Combined_4326.tiff'
output_path = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Reclassed-Urban_4326.tiff'
expression = (
'(A == 21)*10 + '
'(A == 22)*1 + '
'(A == 23)*1 + '
'(A == 24)*2'
)
command = [
'gdal_calc.py',
'-A', input_path,
'--outfile', output_path,
'--calc', expression,
'--type', 'Byte'
]
subprocess.run(command, shell=True)
print("Step 6: Reclass urban completed. (NLCD_" + year + "_" + state + part + "_Reclassed-Urban_4326)")
################################################################ Step 7: Remove clutter and roads from urban ###########################################################
input_path = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Reclassed-Urban_4326.tiff'
output_path = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Urban-Only_4326.tiff'
processing.run(
"grass7:r.neighbors",
{
'input':input_path,
'selection':None,
'method':1, #1=median, 2=mode
'size':7,
'gauss':None,
'quantile':'',
'-c':False,
'-a':False,
'weight':'',
'output':output_path,
'GRASS_REGION_PARAMETER':None,
'GRASS_REGION_CELLSIZE_PARAMETER':0,
'GRASS_RASTER_FORMAT_OPT':'',
'GRASS_RASTER_FORMAT_META':''
}
)
print("Step 7: Remove clutter and roads from urban. (NLCD_" + year + "_" + state + part + "_Urban-Only_4326)")
############################################################## Step 8: Combine grass only and clean urban #########################################################
input_path_a = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Urban-Only_4326.tiff'
input_path_b = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Grass-Only_4326.tiff'
output_path = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Combined-Clean_4326.tiff'
expression = (
'((A > 0) & (B > 0)) * A + '
'((A <= 0) | (B <= 0)) * B'
)
command = [
'gdal_calc.py',
'-A', input_path_a,
'-B', input_path_b,
'--outfile', output_path,
'--calc', expression,
'--NoDataValue', '0'
]
subprocess.run(command, shell=True)
print("Step 8: Combined and clean completed. (NLCD_" + year + "_" + state + part + "_Combined-Clean_4326)")
################################################################## Step 9: Upsample to HD #################################################################
input_path = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Combined-Clean_4326.tiff'
output_path = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Combined-Clean-HD_4326.tiff'
# Open the original raster
ds = gdal.Open(input_path)
gt = ds.GetGeoTransform()
# Extract the original resolution
original_xRes = gt[1]
original_yRes = abs(gt[5])
# Define the percentage to resize by (e.g., 0.50 for 50%, 2.0 for 200%)
percentage = 8.0 # Adjust this as needed
# Calculate the new resolution
new_xRes = original_xRes / percentage
new_yRes = original_yRes / percentage
# Perform the warp (resampling)
gdal.Warp(
output_path,
input_path,
xRes=new_xRes,
yRes=new_yRes,
outputType=gdal.GDT_Byte # Set the output type to uint8
)
print("Step 9: Upsample to. (NLCD_" + year + "_" + state + part + "_Combined-Clean-HD_4326)")
################################################################## Step 10: Smooth all features in original dataset #################################################################
input_path = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Combined-Clean-HD_4326.tiff'
output_path = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Smoothed-HD_4326.tiff'
processing.run(
"grass7:r.neighbors",
{
'input':input_path,
'selection':None,
'method':1, #1=median, 3=mode
'size':11,
'gauss':None,
'quantile':'',
'-c':False,
'-a':False,
'weight':'',
'output':output_path,
'GRASS_REGION_CELLSIZE_PARAMETER':0,
'GRASS_RASTER_FORMAT_OPT':'',
'GRASS_RASTER_FORMAT_META':''
}
)
print("Step 10: Smooth all features in original dataset completed. (NLCD_" + year + "_" + state + part + "_Smoothed-HD_4326)")
################################################################## Step 11: Convert to 8Bit #################################################################
input_path = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Smoothed-HD_4326.tiff'
output_path = path + state + '/data/NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Smoothed-HD-Compressed_4326.tiff'
processing.run(
"gdal:translate",
{
'INPUT':input_path,
'TARGET_CRS':None,
'NODATA':0,
'COPY_SUBDATASETS':False,
'OPTIONS':'',
'EXTRA':'',
'DATA_TYPE':1,
'OUTPUT':output_path,
'OPTIONS': 'COMPRESS=LZW'
}
)
result_urban_layer = QgsRasterLayer(output_path, 'NLCD_' + year + '_' + state + part + '_Smoothed-HD-Compressed_4326')
QgsProject.instance().addMapLayer(result_urban_layer)
print("Step 11: Reclass no-data (nan) to 41. (NLCD_" + year + "_" + state + part + "_Smoothed-HD-Compressed_4326)")
Generating the Terrain using osgdem
Instead of using genVPB.py, you may wish to run osgdem directly.
In the Windows/Docker platform you can send the generate tile command directly to osgdem.exe, one tile at a time.
Using the NLCD raster processing convention from above, following is the the final step after creating the raster and entering bash shell with the windows version of "docker run..."
osgdem --TERRAIN --image-ext png --RGBA --no-interpolate-imagery --disable-error-diffusion --geocentric --no-mip-mapping -t ./data/California-Southern_4326-84-hd-corrected.tiff -d ./SRTM-3/N32W115.hgt -b -115 32 -114 33 --PagedLOD -l 7 --radius-to-max-visible-distance-ratio 3 -o ./output/vpb/w120n30/w115n32/ws_w115n32.osgb
Note: the --image-ext png --RGBA flags are critical to successfully building correctly placed landclasses in the final VPB generated scenery.
If you prefer to run the scenery generation manually, running the VPB osgdem process is described in more detail here: Virtual Planet Builder#Running VPB.
After doing this you should have an output directory containing files of the form output/vpb/w010n50/w004n50/ws_w004n50.osgb, plus a host of sub-directories. Each one of these is a 1x1 tile of terrain.
to leave the container simply type exit.
Packaging the Scenery
Once you have the terrain and line features they should be packaged in a scenery directory in vpb and Terrain sub-directories respectively. E.g.
MyCoolScenery/Terrain MyCoolScenery/vpb
It is good practise to document the data sources used in scenery generation. Some source licenses require attribution of the original data source for anything derived, published or distributed.
To assist in fulfilling these license obligations, you can create a source.xml file in the scenery directory which includes attribution information. This will then be available from within the simulator under Help->Scenery Sources, and may fulfil the attribution requirements of your license. Note that you are responsible for fulfilling any license requirements from the data, not FlightGear.
The format of the file is straightforward:
<?xml version="1.0"?> <PropertyList> <source> <name>Corine Land Cover (CLC) 2018, Version 2020_20u1</name> <link>http://web.archive.org/web/20221112175615/https://land.copernicus.eu/pan-european/corine-land-cover/clc2018?tab=metadata%2A</link> <license>GMES Open License</license> </source> <source> <name>NASADEM Merged DEM Global 1 arc second V001</name> <link>https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/</link> <license>Public Domain</license> </source> <source> <name>OpenStreetMap</name> <link>https://www.openstreetmap.org/copyright</link> <license>Open Data Commons Open Database License</license> </source> </PropertyList>