ATC-pie: Difference between revisions
Mickybadia (talk | contribs) (New release v1.1.0) |
Mickybadia (talk | contribs) (v1.8.8) |
||
| (37 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{forum|83|ATC-Pie support & development}} | {{forum|83|ATC-Pie support & development}} | ||
{{about|the software | {{about|the software and its features|help with installation or configuration|ATC-pie installation guide|a manual on how to use it|ATC-pie user guide}} | ||
{{Infobox Software | {{Infobox Software | ||
| title = ATC-pie | | title = ATC-pie | ||
| logo = ATC-pie-logo.png | | logo = ATC-pie-logo.png | ||
| image = ATC-pie-screenshot- | | image = ATC-pie-screenshot-towerViewing.png | ||
| alt = | | alt = Tower viewing, following a departing aircraft | ||
| developedby = Michael Filhol | | developedby = Michael Filhol | ||
| initialrelease = February 1, 2015 | | initialrelease = February 1, 2015 | ||
| latestrelease = 1. | | latestrelease = 1.8.8 (April 1, 2023) | ||
| writtenin = | | writtenin = Python | ||
| writteninversion = 3 | |||
| os = Any | | os = Any | ||
| platform = Qt5 | | platform = Qt5 | ||
| Line 17: | Line 18: | ||
| type = ATC client | | type = ATC client | ||
| license = GNU GPL v3 | | license = GNU GPL v3 | ||
| website = | | website = http://mickybadia.free.fr/atcpie | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''ATC-pie''' is | '''ATC-pie''' is a free (libre) [[air traffic control]] simulation program with strong ties to [[FlightGear]]. It features: | ||
* solo sessions with AI traffic (incl. voice instruction recognition and pilot read-back); | |||
* "multi-player" network sessions (FlightGear and FSD protocols supported); | |||
* tutorial sessions for teacher supervision of an ATC student. | |||
It is designed to support a maximum range of ATC situations (roles, equipment...), at any world location and for every session type above. All control positions are possible, whether airport-based (TWR, APP, GND...) or en-route (CTR). Equipment may include radar screens, data link, etc. or be limited to binoculars and a view of the airfield. | |||
Its essential goal is realism. It simulates many tasks of real-life ATC such as: | |||
* strip racks and sequence management; | |||
* coordination with neighbouring controllers (handovers, voice phone calls...); | |||
* radar monitoring and identification of traffic; | |||
* vectoring and course/level conflict anticipation; | |||
* flight plan operations; | |||
* CPDLC... | |||
== Screenshots == | |||
= | <gallery mode="packed"> | ||
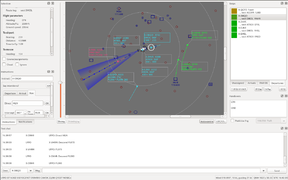
ATC-pie-screenshot-sectorView.png|Sector view around Geneva | |||
ATC-pie-screenshot-soloMode.png|Solo session with three coloured racks | |||
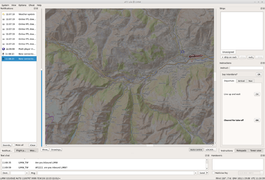
ATC-pie-screenshot-backgroundPixmapDrawing.png|Background image display | |||
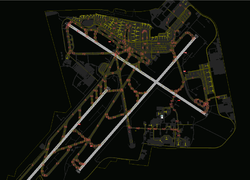
ATC-pie-screenshot-airportCloseUp.png|Depiction of airport tarmac and objects | |||
ATC-pie-screenshot-runwayIncursion.png|Runway incursion detected and highlighted in red | |||
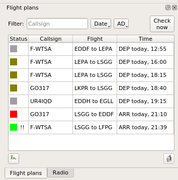
ATC-pie-screenshot-flightPlans.png|Flight plan editor | |||
</gallery> | |||
Visit the [[:Category:ATC-pie screenshots|ATC-pie screenshot category]] for more. | |||
== Detailed feature list == | |||
=== Sessions and environments === | |||
* | Session/connection types: | ||
* | * solo simulation (AI traffic) | ||
* | * FlightGear network connection ([[FGMS]] protocol) | ||
* | * FSD connection (as served by https://github.com/kuroneko/fsd commit bc7d43, latest available in Dec. 2022) | ||
* teaching service (spawn and simulate traffic visible to a connected student) | |||
* student session (control traffic simulated by teacher) | |||
Location modes (available for all sessions): | |||
* | * airport (AD): positions such as TWR, GND, APP, DEP at a selected airfield | ||
* en-route centre (CTR): free positioning of radar, no base airport or runway-related options | |||
* | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" | |||
|+ Feature support by session type | |||
! || Solo || FlightGear || FSD || Tutoring (teacher/student) | |||
* | |- | ||
* | ! ACFT traffic | ||
| AI aircraft generated according to RWY capacities, ACFT equipment, intentions... | |||
| colspan="2" | connected flight sim pilots | |||
| created and simulated by teacher | |||
|- | |||
! ATCs and coordination | |||
| virtual ATCs depending on assumed positions | |||
| colspan="2" | connected ATC clients (full ATC-pie interaction, [[#Interoperability with other software|interoperability with other software]]) | |||
| teacher-configured ATCs | |||
|- | |||
! Voice radio | |||
| voice recognition for instructions (mouse-only also available) and synthesis for pilot read-back | |||
| colspan="2" | [[FGCom-mumble]] integration | |||
| teacher simulates pilots | |||
|- | |||
! ATC phone lines | |||
| N/A | |||
| colspan="2" | integrated Mumble connection | |||
| teacher simulates ATCs | |||
|- | |||
! Flight plans | |||
| local entries only | |||
| interface with the FlightGear ''de facto'' [http://flightgear-atc.alwaysdata.net data base by Lenny64] | |||
| available from network (NB: protocol does not support open/close and only pilots can file/amend FPLs) | |||
| shared virtual online system | |||
|- | |||
! CPDLC | |||
| interpreted subset of instruction messages | |||
| integrated (supported by MP IRC) | |||
| integrated interface with [https://www.hoppie.nl/acars/ Hoppie's ACARS network] | |||
| full simulation by teacher (with WILCO assistance to execute instructions) | |||
|- | |||
! Weather | |||
| randomised and evolving | |||
| real world METAR retrieval | |||
| fetch from server or retrieve real world METAR | |||
| controlled by teacher | |||
|- | |||
! Other specific features | |||
| style="text-align:left" | | |||
* aircraft type and airline choice with custom appearence in tower view | |||
* configurable airspace rules and traffic density, incl. uncontrolled distractors | |||
| style="text-align:left" | | |||
* exact aircraft rendering in views (incl. control surfaces, etc.) | |||
* legacy [[FGCom_3.0|stand-alone FGCom]] alternate possible (although deprecated) | |||
| style="text-align:left" | | |||
* frequency tuning system for radio text chat | |||
* text ATIS repeatedly sent through radio chat on recorded frequency | |||
| style="text-align:left" | | |||
* traffic snapshots and recall to repeat situations with the student | |||
* individual aircraft freeze | |||
|} | |||
=== ATC surveillance === | |||
* | Radars and tracking: | ||
* | * SSR mode capability selection (none/A/C/S) | ||
* | * primary radar toggle | ||
* | * traffic identification assistant | ||
* | * position/track vs. strip assignment mismatch warning system | ||
* | * route/vector conflict anticipation | ||
* separation incident alarm | |||
* runway occupation/incursion detection | |||
Tower view in airport mode (rendered by FlightGear): | |||
* view of airport, aircraft, weather, time of day | |||
* | * start internal process or use externally running instance | ||
* | * control panel to orient/zoom view or follow aircraft | ||
* | * additional views can be connected (for multiple camera angles) | ||
Other: | |||
* | * radio direction finding (RDF) and integration to radar | ||
* multiple weather (METAR) station monitor | |||
* | |||
=== Traffic management === | === Traffic management === | ||
Strips | Strips and racks: | ||
* | * user-defined strip racks with configurable colours (for linked radar contacts) and ATCs to receive from | ||
* | * runway boxes with automatic RWY separation timers | ||
* | * loose strip bays with customisable backgrounds | ||
Flight plans and routes: | |||
* | * flight plan system (file, edit, open, close, publish/retrieve online) | ||
* | * world route suggestions, presets, analysis, radar drawing and world map view | ||
* departure clearance assistant | |||
* | * automatic strip printing for expected departures or arrivals (from FPLs) | ||
Radar tools: | |||
* | * convenient mouse input for instructions (vectors, taxi...) and CPDLC integration | ||
* | * approach spacing hints (estimated touch-down time difference, sequence optimisation suggestions) | ||
* | * quick point-to-point heading and distance measuring tool | ||
* direct text annotation of radar screen | |||
* flag/unflag (highlight) radar targets | |||
=== Communications === | === Communications === | ||
With aircraft: | |||
* | * voice radio with 8.33 kHz frequency spacing, multiple radio transmissions and monitoring | ||
* ATIS recording | * [[ATIS]] recording and reminder alarm (see [[:File:ATC-pie-screenshot-ATISdialog.png|dialog]] with pre-filled notepad) | ||
* | * [[controller-pilot data link communication]] (CPDLC), incl. DEP clearance delivery, multi-element messages... | ||
* | * text radio chat with preset messages, auto-completion, predefined and custom aliases (context-sensitive replacements), sender blacklist | ||
ATC coordination: | |||
* | * strip exchange (handovers) | ||
* CPDLC authority transfers | |||
* | * telephone lines and switchboard (direct voice communication) | ||
* | * text messaging (private channels and general ATC chat room) | ||
* | * "who has?" requests | ||
== | === Other === | ||
Misc. tools: | |||
* world airport, map navpoint and AD parking position browsing/indicating | |||
* aeronautical unit conversion calculator | |||
* custom alarm clocks with quick keyboard timer start | |||
* general and location-specific notepads restored between sessions | |||
GUI: | |||
* multiple window workspace (radar screens, strip racks and bays) saved by location | |||
* floatable/dockable panels and toolbars (see [[:File:ATC-pie-screenshot-toolbars.png|screenshot]]) and layout save/restore | |||
* notification system combining selectable sounds, status bar messages and time-tagged history | |||
* customisable style and colours | |||
Data sources: | |||
* airport and navigation data sourced in the [http://developer.x-plane.com/docs/specs X-Plane] format (old world-wide default file set provided but custom imports recommended) | |||
* editable aircraft data base (ICAO designators, cruise speeds, WTC, etc.) | |||
* custom radar background images and hand drawings (EuroScope/[http://www.vatsim.net VATSIM]/IVAO "sector file" conversion tool included) | |||
* ground elevation maps (can be generated automatically with a provided script if FlightGear terrain data available) | |||
* manual magnetic declination input | |||
== Interoperability with other software == | |||
=== | === OpenRadar === | ||
[[ | [[OpenRadar]] is another stand-alone program able to connect to FlightGear networks. ATC-pie and OpenRadar's philosophies differ in several ways: | ||
* OpenRadar's basic processing unit is the FGMS callsign, whereas ATC-pie's is the strip; | |||
* OpenRadar's concept of handover is based on a shared notion of aircraft ownership, whereas ATC-pie allows any controller to pull out a strip and write a callsign on it; | |||
* | * in OpenRadar, a handover must be acknowledged by the receiver for the sender to lose ownership and for all neighbouring users to see it complete, whereas ATC-pie considers that a strip sent is gone and assumed to land on the receiver's rack, without anybody else necessarily to know. | ||
For most interactions to work in FlightGear sessions while respecting both approaches as much as possible, the following principles and restrictions apply to strip exchange between the two programs: | |||
* ATC-pie users can only hand over strips to OpenRadar that are linked to a radar contact; | |||
* | * aircraft under ATC-pie control are not shown as "owned" to OpenRadar users; | ||
* | * handovers from ATC-pie will fail if an OpenRadar user is claiming ownership on the linked radar contact; | ||
* when sending to ATC-pie controllers, OpenRadar users will see their transfers acknowledged straight away, unconditionally. | |||
Callsign handover policy: | |||
* OpenRadar to ATC-pie: FGMS callsign will appear on the strip, as if the sender had filled the detail herself; | |||
* ATC-pie to OpenRadar: callsign resolved for the receiver, sender's entry will reappear next time ATC-pie handles the strip; | |||
* pie-to-pie handovers through OpenRadar's service: strip detail preserved, whether present or absent. | |||
Features not supported by OpenRadar: | |||
* | * wake turbulance category on strips (but detail preserved for ATC-pie clients later receiving the strip); | ||
* | * ATC text messaging; | ||
* | * ATC phone lines; | ||
* CPDLC transfers. | |||
Who-has requests are fully supported. | |||
== | === Euroscope === | ||
Euroscope is a popular program to control on VATSIM, a flight simulation network whose protocol is historically based on FSD. It has been increasingly tailored for VATSIM, although for a long time it allowed also to connect to "plain" (non-VATSIM) FSD servers. Operability outside of VATSIM is now discontinued all together, but older versions of Euroscope are still around and connecting to FSD networks. ATC-pie is able to interact with them in FSD sessions, but only to a limited extent: | |||
* sending a strip to Euroscope will result in a loss of all strip details but the callsign (which must be connected), the only information left to the recipient being the FPL details for that callsign if any (strip changes made after FPL data retrieval are therefore lost); | |||
* receiving a strip from Euroscope is supported, but the sender will see the hondover pending (never "assumed"); | |||
* who-has requests will remain unanswered by Euroscope; | |||
* there are no integrated phone lines to Euroscope clients. | |||
[[Category:ATC-pie]] | [[Category:ATC-pie]] | ||
[[Category:ATC clients]] | [[Category:ATC clients]] | ||
[[Category:Air Traffic Control]] | |||
Latest revision as of 08:27, 2 April 2023
| The FlightGear forum has a subforum related to: ATC-Pie support & development |
 | |
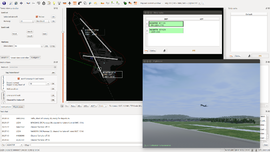 Tower viewing, following a departing aircraft | |
| Developed by | Michael Filhol |
|---|---|
| Initial release | February 1, 2015 |
| Latest release | 1.8.8 (April 1, 2023) |
| Written in | Python (Version 3) |
| OS | Any |
| Platform | Qt5 |
| Development status | Active |
| Type | ATC client |
| License | GNU GPL v3 |
| Website | |
ATC-pie is a free (libre) air traffic control simulation program with strong ties to FlightGear. It features:
- solo sessions with AI traffic (incl. voice instruction recognition and pilot read-back);
- "multi-player" network sessions (FlightGear and FSD protocols supported);
- tutorial sessions for teacher supervision of an ATC student.
It is designed to support a maximum range of ATC situations (roles, equipment...), at any world location and for every session type above. All control positions are possible, whether airport-based (TWR, APP, GND...) or en-route (CTR). Equipment may include radar screens, data link, etc. or be limited to binoculars and a view of the airfield.
Its essential goal is realism. It simulates many tasks of real-life ATC such as:
- strip racks and sequence management;
- coordination with neighbouring controllers (handovers, voice phone calls...);
- radar monitoring and identification of traffic;
- vectoring and course/level conflict anticipation;
- flight plan operations;
- CPDLC...
Screenshots
Visit the ATC-pie screenshot category for more.
Detailed feature list
Sessions and environments
Session/connection types:
- solo simulation (AI traffic)
- FlightGear network connection (FGMS protocol)
- FSD connection (as served by https://github.com/kuroneko/fsd commit bc7d43, latest available in Dec. 2022)
- teaching service (spawn and simulate traffic visible to a connected student)
- student session (control traffic simulated by teacher)
Location modes (available for all sessions):
- airport (AD): positions such as TWR, GND, APP, DEP at a selected airfield
- en-route centre (CTR): free positioning of radar, no base airport or runway-related options
| Solo | FlightGear | FSD | Tutoring (teacher/student) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACFT traffic | AI aircraft generated according to RWY capacities, ACFT equipment, intentions... | connected flight sim pilots | created and simulated by teacher | |
| ATCs and coordination | virtual ATCs depending on assumed positions | connected ATC clients (full ATC-pie interaction, interoperability with other software) | teacher-configured ATCs | |
| Voice radio | voice recognition for instructions (mouse-only also available) and synthesis for pilot read-back | FGCom-mumble integration | teacher simulates pilots | |
| ATC phone lines | N/A | integrated Mumble connection | teacher simulates ATCs | |
| Flight plans | local entries only | interface with the FlightGear de facto data base by Lenny64 | available from network (NB: protocol does not support open/close and only pilots can file/amend FPLs) | shared virtual online system |
| CPDLC | interpreted subset of instruction messages | integrated (supported by MP IRC) | integrated interface with Hoppie's ACARS network | full simulation by teacher (with WILCO assistance to execute instructions) |
| Weather | randomised and evolving | real world METAR retrieval | fetch from server or retrieve real world METAR | controlled by teacher |
| Other specific features |
|
|
|
|
ATC surveillance
Radars and tracking:
- SSR mode capability selection (none/A/C/S)
- primary radar toggle
- traffic identification assistant
- position/track vs. strip assignment mismatch warning system
- route/vector conflict anticipation
- separation incident alarm
- runway occupation/incursion detection
Tower view in airport mode (rendered by FlightGear):
- view of airport, aircraft, weather, time of day
- start internal process or use externally running instance
- control panel to orient/zoom view or follow aircraft
- additional views can be connected (for multiple camera angles)
Other:
- radio direction finding (RDF) and integration to radar
- multiple weather (METAR) station monitor
Traffic management
Strips and racks:
- user-defined strip racks with configurable colours (for linked radar contacts) and ATCs to receive from
- runway boxes with automatic RWY separation timers
- loose strip bays with customisable backgrounds
Flight plans and routes:
- flight plan system (file, edit, open, close, publish/retrieve online)
- world route suggestions, presets, analysis, radar drawing and world map view
- departure clearance assistant
- automatic strip printing for expected departures or arrivals (from FPLs)
Radar tools:
- convenient mouse input for instructions (vectors, taxi...) and CPDLC integration
- approach spacing hints (estimated touch-down time difference, sequence optimisation suggestions)
- quick point-to-point heading and distance measuring tool
- direct text annotation of radar screen
- flag/unflag (highlight) radar targets
Communications
With aircraft:
- voice radio with 8.33 kHz frequency spacing, multiple radio transmissions and monitoring
- ATIS recording and reminder alarm (see dialog with pre-filled notepad)
- controller-pilot data link communication (CPDLC), incl. DEP clearance delivery, multi-element messages...
- text radio chat with preset messages, auto-completion, predefined and custom aliases (context-sensitive replacements), sender blacklist
ATC coordination:
- strip exchange (handovers)
- CPDLC authority transfers
- telephone lines and switchboard (direct voice communication)
- text messaging (private channels and general ATC chat room)
- "who has?" requests
Other
Misc. tools:
- world airport, map navpoint and AD parking position browsing/indicating
- aeronautical unit conversion calculator
- custom alarm clocks with quick keyboard timer start
- general and location-specific notepads restored between sessions
GUI:
- multiple window workspace (radar screens, strip racks and bays) saved by location
- floatable/dockable panels and toolbars (see screenshot) and layout save/restore
- notification system combining selectable sounds, status bar messages and time-tagged history
- customisable style and colours
Data sources:
- airport and navigation data sourced in the X-Plane format (old world-wide default file set provided but custom imports recommended)
- editable aircraft data base (ICAO designators, cruise speeds, WTC, etc.)
- custom radar background images and hand drawings (EuroScope/VATSIM/IVAO "sector file" conversion tool included)
- ground elevation maps (can be generated automatically with a provided script if FlightGear terrain data available)
- manual magnetic declination input
Interoperability with other software
OpenRadar
OpenRadar is another stand-alone program able to connect to FlightGear networks. ATC-pie and OpenRadar's philosophies differ in several ways:
- OpenRadar's basic processing unit is the FGMS callsign, whereas ATC-pie's is the strip;
- OpenRadar's concept of handover is based on a shared notion of aircraft ownership, whereas ATC-pie allows any controller to pull out a strip and write a callsign on it;
- in OpenRadar, a handover must be acknowledged by the receiver for the sender to lose ownership and for all neighbouring users to see it complete, whereas ATC-pie considers that a strip sent is gone and assumed to land on the receiver's rack, without anybody else necessarily to know.
For most interactions to work in FlightGear sessions while respecting both approaches as much as possible, the following principles and restrictions apply to strip exchange between the two programs:
- ATC-pie users can only hand over strips to OpenRadar that are linked to a radar contact;
- aircraft under ATC-pie control are not shown as "owned" to OpenRadar users;
- handovers from ATC-pie will fail if an OpenRadar user is claiming ownership on the linked radar contact;
- when sending to ATC-pie controllers, OpenRadar users will see their transfers acknowledged straight away, unconditionally.
Callsign handover policy:
- OpenRadar to ATC-pie: FGMS callsign will appear on the strip, as if the sender had filled the detail herself;
- ATC-pie to OpenRadar: callsign resolved for the receiver, sender's entry will reappear next time ATC-pie handles the strip;
- pie-to-pie handovers through OpenRadar's service: strip detail preserved, whether present or absent.
Features not supported by OpenRadar:
- wake turbulance category on strips (but detail preserved for ATC-pie clients later receiving the strip);
- ATC text messaging;
- ATC phone lines;
- CPDLC transfers.
Who-has requests are fully supported.
Euroscope
Euroscope is a popular program to control on VATSIM, a flight simulation network whose protocol is historically based on FSD. It has been increasingly tailored for VATSIM, although for a long time it allowed also to connect to "plain" (non-VATSIM) FSD servers. Operability outside of VATSIM is now discontinued all together, but older versions of Euroscope are still around and connecting to FSD networks. ATC-pie is able to interact with them in FSD sessions, but only to a limited extent:
- sending a strip to Euroscope will result in a loss of all strip details but the callsign (which must be connected), the only information left to the recipient being the FPL details for that callsign if any (strip changes made after FPL data retrieval are therefore lost);
- receiving a strip from Euroscope is supported, but the sender will see the hondover pending (never "assumed");
- who-has requests will remain unanswered by Euroscope;
- there are no integrated phone lines to Euroscope clients.